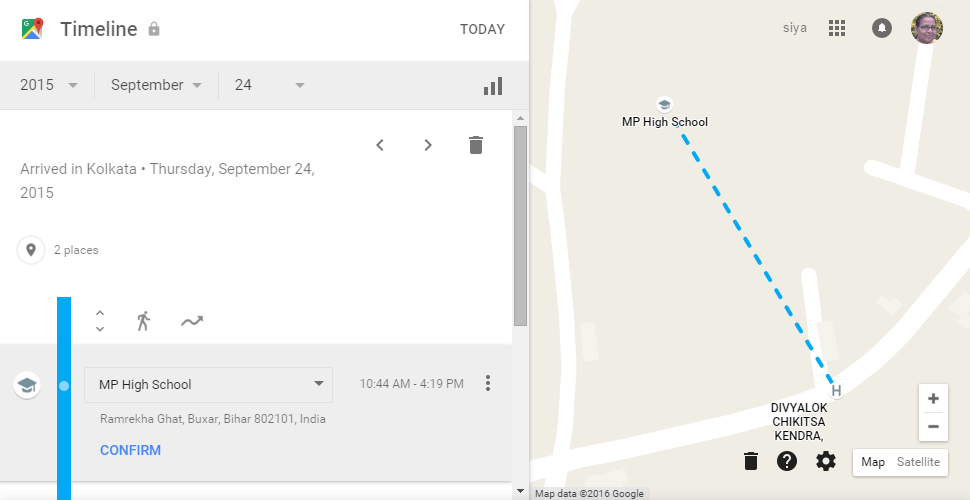
When the time comes
to change your worn out OEM tyre for your motorbike we get confused as to what
to buy. Often the grip in wet conditions reduces as much as 2/3rd of the dry
grip on tarmac.
While selecting
tyres we need to consider the following points:
1) What type of grip
you want - Dry/Wet tarmac, Slush, Gravel, loose soil?/Type and depth of tread
pattern.
2) Tubeless or
tubetype
3) Load rating.
4) Rim size.
5) Clearance
between Swing arm and the tyre. Extent of Modifications required to fit in your
favourite fatter tyre.
6) Compound of
tyre(Soft/Hard) used in manufacturing the tyre.
7) Profile of tyre
- Round/Flat.
8) Width of
tyre/Wider contact patch.
Point No. 6 is the
most important point while purchasing any tyre.
1)Type of grip you
want - [Dry/Wet tarmac], [Slush, Gravel, loose soil]
If you want dry
grip on tarmac you need tyres which would give maximum contact area with the
road that means a tyre with no tread grooves at all! also called Slick tyres as
used in racing.Slick tyres also require a lot of warm up before they start
gripping so they are nearly banned for on-road usage.These tyres will be quite
bad in wet on-road conditions also because they don't have any grooves which
will draining out water during wet operation. Slush, Gravel, Loose soiled will
require a higher depth tread pattern and like a button(like motocross bike
tyres). The more looser the soil the more the distance between two
studs/buttons. A Dual purpose tyre will have closely packed buttons because
they have to perform good on tar road as well as little off-roading and so
contact patch needs to be good for more grip. A motocross type tyre will have
very less contact patch and so will perform poorly on tarmac but the studs will
grip the loose soil(sort of a positive contact) better and so good grip in
off-road conditions.
2) Tubeless(TL) or
tubetype(TT):
If you are having
alloys in your bike then one should go for tubeless tyres. Tubeless tyres have
one advantage that in case of punctures they dont leak air abruptly(also called
as "burp" -lingo) and will deflate slowly. For repairing a TL one
need not remove the wheel from the motorbike.It can be repaired on the bike
itself. So easy to repair a big boon for long distance tourers. IMPORTANT: DO
NOT FIT TUBETYPE TYRE AS TUBELESS ON WHEEL RIM. IT CAN CAUSE ACCIDENT.
3) Load rating:
It is mentioned on
the sidewall of the tyre and it represents the capacity of the tyre to take the
weight of the bike. Do not go for a lower Load rating than that is mentioned on
your OEM tyre.
4) Rim Size and
Tyre width:
Tyres are built for
a particular RIM size. Its dangerous to fit any random tyre on any random rim.
Eg. A tyre specification is 120/80 x 17 means a Tyre width of 120 mm, a Tyre
height(radial distance from rim to the outer surface of the tyre.) of 80% of 120
mm and 17 is the Rim Diameter in inches. A tyre specification does not mention
rim width. Eg: Rim width: 2.15j means 2.15 inches. For eg. the maximum tyre
width a 2.15j rim can support is 120 mm.There are various charts available on
internet to suggest the fattest tyre your existing rim can support. Confusing!
So the thumb rule is you can go to a next bigger width of tyre on your
motorcycle than what is provided by your OEM. If my motorcycle came with a 110
mm width tyre fitted on 2.15j rims the max I can go for is 120 mm.
5) Clearance
between Swing arm and the tyre. Extent of Modifications required to fit in your
favourite fatter tyre.
This clearance is
very important as the tyre can rub your swingarm or your bikes body parts
especially during the bike going through a pothole. And what if the tyre
punctures and there is no space for the flattened tyre. I am still to find out
the acceptable gap between the swing arm and the tyre but I feel a minimum of
7-8 mm will be required for all the conditions the tyre has to go through.(The
tyre expands width wise while going through a pothole). You can adjust a fatter
tyre in your existing bike by pulling the rear tyre more rearwards by adjusting
the chain. You might be required to fit an additional link in the chain to do
so. You will also might be required to cut the chain guard to make clearance. I
would never recommend cutting the swing arm to make space for fatter tyre as it
will lead to serious problems with the rigidity-read stability of the bike and
also the reliability of the bike.
6) Compound of
tyre(Soft/Hard) used in manufacturing the tyre.
Compound of the
tyre is one of the most important even more important than contact patch. A
softer tyre compound has better grip than a similar hard compound tyres. But a
softer compound tyre will wear faster leading to less life of the tyre. A
harder compound tyre has less on-road grip but will last longer. On pure loose
soil as in off-roading the compound of the tyre will not matter much but the
tread depth and tread pattern will matter more.(Read button type). A Dual
purpose tyre will have a right blend of the Soft and Hard Compound, Hard enough
so that it lasts long during the off-roading and at the same type soft enough
to get a good grip on tarmac which is quite difficult to get.
How to check: Press
your fingers nail into a hard and soft compound tyre and you will notice that
the depression formed will be more and will also take more time to recover in a
soft compound tyre. Also I observed that a soft compound tyre when rubbed hard
with your thumb will give out flakes(similar to your pencil eraser) and the
surface will be rough to touch. A hard compound tyres surface will be smooth
with a nice finish which we don't want it to be!
7) Cross-section
Profile of tyre - Round/Flat.
Tyre which are
found on race bikes will have a more rounder profile which is good for
cornering at high-speeds. Tyres which are found on touring bikes will have more
of a flat profile to get better contact patch while straight-ahead driving
position. One more point to be noted here is that a thinner rim width will make
a tyre more rounder and a higher rim width will make the tyre more flat so one
might need to select the correct rim width size to get the correct tyre profile
he desires. The tyre profile depends on the tyre make the tyre manufacturer can
make a tyre which is mounted on thinner rim to have a flat profile where as a
tyre which is mounted on wider rim to have a rounder profile so it all depends
on the type of tyre. One should always check whether a certain tyre width can
be mounted on a particular rim width from the manufacturer itself.
8) Width of
tyre/Wider contact patch.
We always want a
wider contact patch at the contact between the tyre and road contact point. Now
one would question that Mu Friction coefficient is not dependent on area but
then that is only true of ideal bodies which don't deform.For those bodies
which deform like the tyre rubber the above law does not hold true and the law
of micro asperities rules the situation. So the more wider the tyre the more
grip it will give. But remember a wider/heavier tyre and more so with a soft
compound due to more grip is bound to reduce your bikes acceleration and also
to some extent fuel efficiency.
At the moment we will
replace the tires of vehicles, usually we just say the size of tire that we
will change or buy, ie the size of 2.75-17 or 100/90-18. Because
the parameter that indicates the size of the width, thickness and diameter, but
in fact there are many codes and symbols that bikers should know in order to
get a tire that meets the specifications chill and know the safe limits for
consumption.
We see from the most common standard used for a tire.  Tire Size
Tire SizeTire size usually use the metric system (metric system) or system-inch (inch system). As an illustrative example tire has a code: 100/90-18, and 2.50-17
how to read it?
100/90-18 tire uses the metric system mean the first number is the size of tire width, the second number after the slash (/) adalan ratio in percent between the width and height of the tire and the third digit after the sign - is the diameter of the rim / wheel. So the size of the tires with 100/90-18 if the translated code is 100 mm tire width, height, tires 90% x 100 = 90 mm and diameter of the tire or wheel size / rim 18 inches.
Tires 2.50-17 inch system so the size is the width of 2.5-inch tires, if converted to mm, 1 inch = 2:54 a 63.4 mm tire width, height of the tire because the second number after the slash is not considered the ratio is 100% so high 2:50 and diameter in inches tire or rim size 17 inch / 17 inch rim.
Age ProductionIn one side of the tire usually printed four-digit code that indicates when the tire is produced. For example, the 2108 figures can be read the first two digits indicate the week, the last two digit year of manufacture. So the code above is a tire produced in week-21 in 2008. Code production age to note how long the tires can be stored, who fear that affect the performance of the tire itself
Front or Rear Tire CodeTo code the use of the front tires or rear tires usually are written with the letter (alphabet) code "F" means front tire to front tire while "R" rear tire to rear tire. Usually there are differences in the form of development / pattern front and rear tires due to the different functions for the front tires as the wheel and if the rain should be able to drain the water so the front tires usually have a flow of water. While the rear tires to drive the function requires a large torque so that the traction is needed so the rear tires usually larger size and has no water flow.
But sometimes we also like to see the rear tires have water flow only the larger size difference alone.
Maximum speed codeMaximum speed of code written by the code letter, which indicates the limit
maximum of a tire driven on for 1 hour with a load according to standard specifications.
Table Maximum speed (km/h)
Case in point : Honda Beat scooter tire brands Federal code 80/90-14 M / C 40P. The letter P that is behind the number (40P) showed that the maximum speed. Appropriate table above shows P is the maximum speed of 150 km / hour.
The Code Used Compound
Compound Code tire letter written in code, which indicates that the tire compound has a soft to hard. Code "S" indicates soft soft compound, "M" indicates medium compound medium and "H" hard means hard tire compound. Selection of tire compound depending on the needs for example for the road race which usually use a soft compound tire with a softer compound is soft and sticky stick to the asphalt, but because it is soft then the tire will quickly run out. While the medium is usually used for day to day. If a tire brand Batllax with code BT 92 F Radial 120/70 R17 M / C 54H, code M / C that's what tire compound showed moderate.
The Direction of Tire Rotation
Direction of rotation or tire rotation is shown by an arrow (Arrow), installation of tires must be in accordance with the direction of the arrow for the direction this development will be the perfect tires stick to the asphalt, or pouring water on wet roads as well as
get good traction. If the installation of inverted tire will not stick to the road and less well traksinya so the tires feels more slippery which could endanger the rider.
Maximum Load Tires
Indication of the maximum load that can be retained by the tire in a cold state
usually included in Diding tires. There have written direct bebanya also are using index numbers.
Written direct written eg Max. Load 212 kg (467 LBS) AT 280 KPa (41 psi) Cold can be read: the tire to hold the maximum load 212 kg or 467 lbs with a maximum wind pressure of 41 psi in cold conditions (vehicle not used)
Using index numbers :
(73W) V280 73 numbers are index numbers that have a standard maximum load 365 kg.
Table below the maximum load index (kg).
• 30 = 106, 31 = 109, 32 = 112.33 = 115, 34 = 118, 35 = 121, 36 = 125, 37 = 128, 38 = 132, .39 = 136
• 40 = 140, 41 = 145, 42 = 150, 43 = 155, 44 = 160, 45 = 165, 46 = 170, 47 = 175, 48 = 180, 49 = 185
• 50 = 190, 51 = 195, 52 = 200, 53 = 206, 54 = 212, 55 = 218, 56 = 224, 57 = 230, 58 = 236, 59 = 243
Type of Tire
On the side of the tire wall is usually also included these types of tires such as TT = Tube Type or TL = tubeless. Tube-type tire means the tire using tire inner tube, medium or radial tubeless tires are not needed in again.
Symbol Triangle
Triangle symbol is called Thread Indication (TWI) or limit the use of indicators.
Picture a triangle on the side of the tire wall is the final limit of tire grip or plot, if plot tires have been eroded or thin sdudah because the use of the tire should be replaced because it was not safe anymore.
Symbol Color Line
The symbol of this color line is the layer of development that has not been used to indicate the tire was new. Because the outer layer of these tires on the development / pattern so if the old tires will wear out. Color line there is one but there are also more than one color, and each manufacturer usually has a different color eg white, red, yellow, blue and green.
Symbols Balance
Symbols balance is usually in the form of dots on the tire wall, mark a round with different colors for each manufacturer eg yellow, red or blue. Signs of this balance must be considered when setting up the tires, because the lightest itulan point of each tire, at that point also the position of valve must be parallel. Because the tire valve is a heavy point of the tire.
Tire Structure
Not all manufacturers specify tire tire structure, but for good-quality tire manufacturers usually include them. For example: Tread: 4 nylon, side wall: 2 nylon.
* Tread tire tread is the part that directly intersect with the asphalt, must be strong against impact, which can damage the tire puncture. provide power sticks to the asphalt and tire durability due to friction. So Tread tire comprises four layers of nylon.
* Side wall is the wall of the left and right side tires. Functioning as a crutch ban.Jadi tire side wall is composed of 2 layers of nylon.
References :
1. http://www.mouthshut.com/review/Advice-on-Choosing-Bike-Tyres-review-molrtspnmr
2. http://www.zephyr39.co.cc/